Table of Contents
Can you imagine a world without the convenience of flipping a switch for a light or plugging in your favorite appliance? An electrical wiring system is like the invisible backbone that powers your modern life. It safely carries electricity throughout buildings, allowing you to use all sorts of devices and systems.
So, do you want to learn more about the different types of electrical wiring? Whether you are planning a home renovation or just want to be more informed about your home’s electrical system, this blog is the perfect place to start. It dives into everything you need to know about electrical wiring, from the basics to the more advanced stuff.
So, sit back, relax, and get ready to amp up your knowledge about electrical wiring!
What is Electrical Wiring?
So, what precisely constitutes electrical wiring? It is the process of connecting cables and wires to different appliances such as fuses, switches, sockets, lights, fans, and so on. These are all connected to the main distribution board. It is the large structure on the utility pole that keeps everything turned on.
But here’s the thing: this isn’t simply a free-for-all. Authorities have established norms and regulations that must be observed while installing electrical wiring systems. If you don’t follow these criteria or work carelessly, you might end up with short circuits or electric shocks.
Before any home or business begins wiring planning, there is a lot to consider! The sort of building involved, as well as the ceiling structures, walls, and floors where devices will be mounted, must all be carefully planned!
What are the Different Types of Wiring Methods Based on Installation?
Here are the 5 types of electrical wiring systems you should know about:
- Cleat Wiring
- Casing and Capping Wiring
- Batten Wiring (CTS or TRS)
- Conduit Wiring (Surface or Concealed)
- Lead Sheathed Wiring
What are the Exposed Electrical Wiring Systems?
Exposed wiring methods, as the name suggests, involve the installation of electrical wiring where the wires and cables are visible and not concealed within walls, ceilings, or floors. This method provides a practical solution for electrical installations in areas where concealing the wiring is not feasible.
Let’s take a closer look at the three types of exposed wiring methods and their advantages and disadvantages.
-
Cleat Wiring
Cleat wiring involves the use of insulated wires that are supported by porcelain, wooden, or plastic supports, known as cleats. These supporters are fixed on walls or ceilings. This method is known for its simplicity and ease of installation.
- Pros of Cleat Wiring
Cleat wiring has some significant advantages. It’s a simple and cost-effective system since the cables are exposed. This wiring makes it easy to locate and fix faults quickly. Installation is straightforward, and customization options are available for changes or additions.
- Cons of Cleat Wiring
However, there are some downsides to cleat wiring. The appearance may not be very appealing. Also, this wiring method is more prone to fire risks and wear due to exposure to weather elements. Additionally, it can only be used at low temperatures of 250/440 Volts.
-
Batten Wiring
Batten wiring utilizes single-core cables that are run along wooden battens fixed on walls or ceilings. This method is commonly used in domestic and small-scale installations.
- Pros of Batten Wiring
Batten wiring has its own set of advantages! It offers a simple installation process with lower costs compared to traditional systems while having an attractive appearance and easy repairs.
- Cons of Batten Wiring
This wiring may not be suitable for humid or outdoor environments as there is a higher risk of fires due to exposure factors such as heat, dust & smoke. Moreover, batten wiring is without resistance features against external wear & tear effects – plus heavy electrical cables won’t work here!
-
Casing and Capping Wiring
The casing and capping wiring method involves the use of cables encased in wooden casings and covered with a protective cap. This method provides a neat and organized solution for surface wiring installations.
- Pros of Casing & Capping Wiring
It offers aesthetic appeal and added protection to the wiring. Casing capping also provides various other benefits, granting you long-term durability, besides being resistant to oil, steam rain, etc., which means there is no risk of electric shock either!
- Cons of Casing & Capping Wiring
Nonetheless, a notable disadvantage of this type of electrical wiring is that it may be more labor-intensive during the installation process compared to other methods. This system poses astounding challenges when situated in acidic, alkaline humidity.
It surpasses costly maintenance by providing material scarcity complications. Wood damage by white ants even threatens the casing & capping wiring!
What Types of Wiring Falls Under Concealed Electrical Wiring System?
Concealed wiring methods involve installing electrical wiring within walls, ceilings, or floors where the wires and cables are hidden behind finished surfaces such as drywall, plaster, or flooring materials.
This technique is used to protect and hide the wiring. It provides a neater and more aesthetically pleasing appearance while ensuring safety and compliance with electrical codes. Here are the two main types of concealed wiring methods, along with their advantages and disadvantages.
1. Conduit Wiring
Conduit wiring is a method of electrical wiring where insulated wires are enclosed within metal or plastic conduits. This protects against physical damage and moisture while allowing for easy replacement or modification of wiring.
Types of Conduit Wiring
- Surface Conduit Wiring
Surface conduit wiring, as the name suggests, involves the installation of conduits on the surface of walls or ceilings. This type of wiring is commonly used in situations where it may not be feasible or practical to conceal the conduits within the structure.
Surface conduit wiring provides easy access for maintenance and repairs. That makes it a popular choice for commercial and industrial settings.
- Concealed Conduit Wiring
Concealed conduit wiring, on the other hand, involves routing the conduits within the walls, ceilings, or floors of a building. This type of wiring offers a clean and aesthetically pleasing finish since the conduits are hidden from view. Concealed conduit wiring is often preferred in residential and commercial spaces where a seamless, uncluttered look is desired.
Types of Electrical Conduits
- Metallic Conduit
Metallic conduits are made from materials such as steel or aluminum. They are used to protect electrical wires from physical damage and electromagnetic interference. These conduits provide excellent shielding and can withstand high-temperature environments. They are suitable for industrial applications where robustness is essential.
- Non-Metallic Conduit
Non-metallic conduits, also known as PVC conduits, are made from PVC (polyvinyl chloride) material. They are lightweight, flexible, and resistant to corrosion, making them an ideal choice for residential and commercial wiring installations.
Non-metallic conduits are easy to install and are often used in applications where cost-effectiveness and versatility are important factors.
- Size of Conduit
The conduit pipes come in various sizes, ranging from 13 mm to 63 mm in diameter or 1/2 inch to 2 inches.
Advantages of Conduit Wiring
Conduit wiring comes with several advantages. Firstly, it is the most secure wiring method available. It provides a stunning appearance while ensuring the vehicle’s cables’ insulation is not harmed. This type of wiring is resistant to corrosion and fire. So, they are suitable for humidified, chemically affected, and smoky environments.
Additionally, there are no dangers of electric shock associated with conduit wiring due to its well-liked and dependable nature. Moreover, this system provides long-lasting sustainability.
Disadvantages of Conduit Wiring
However, there are some disadvantages that need consideration as well. Conduit Wiring can be costly compared to other systems. There could also be challenges in locating potential flaws in the wirings, and installation may not always be straightforward.
As a result, managing additional connections in the future might become complex, leading to electric shock hazards.
2. Lead Sheathed Wiring
Lead-encased wiring is a kind of wire in which the conductors are insulated with VIR and wrapped in a lead aluminum alloy outer sheath that contains around 95 percent lead. This metal wrapping protects the wires against mechanical damage, moisture, and corrosion induced by the environment.
The whole lead sheath covering is electrically continuous and grounded at the entrance point to protect against electrolytic action caused by leaking current. TRS wiring installs lines on wooden battens using link clips.
Advantages of Lead Sheathed Wiring
Lead-sheathed wire has a long lifespan. Moreover, it has got good looks.
Disadvantages of Lead Sheathed Wiring
However, there are certain drawbacks to using lead-encased wire, such as its higher cost. Also, it is challenging to locate defects in lead sheath wiring.
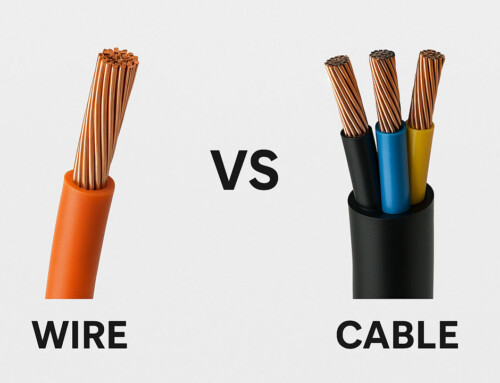
What Types of Electrical Cables are Used for Houses and Buildings?
If you’ve ever wondered about the different sorts of cables used in electrical systems, you’re in the right place. Let’s explore five common types that you might encounter.
-
NM-B Cable (Non-metallic)
The NM-B cable, also known as non-metallic cable, is a versatile option commonly used for residential wiring. It consists of two or more insulated conductors enclosed in a plastic sheath, making it suitable for interior wiring and dry locations.
-
Armored Cable (BX)
Armored cable, commonly referred to as BX, is a robust and flexible option designed for areas where mechanical protection is required. It features a flexible metal armor layer that provides additional security, making it ideal for industrial and commercial applications.
-
Underground Feeder Cable (UF)
Underground feeder cable, or UF cable, is specifically designed for underground use. Its moisture-resistant and direct burial capabilities make it ideal for outdoor and below-grade installations, such as outdoor lighting and underground circuits.
-
Low-Voltage Wiring
Low-voltage wiring involves electrical wiring with a voltage lower than standard household wiring, typically below 120 volts. This type of cable is commonly utilized for specialized systems like doorbell circuits, thermostat wiring, security systems, and audio/video setups.
It uses smaller gauge wires and includes cables such as thermostat wires for HVAC systems, bell wires for doorbells, and coaxial or Ethernet cables for audio/video and networking applications.
-
Solar Cables
Solar cables are specifically designed for use in photovoltaic (PV) systems, commonly known as solar power systems. These specialized cables are used to connect solar panels to other components of the system, such as inverters, batteries, or the electrical grid.
They are engineered to withstand outdoor environmental conditions, including sunlight, extreme temperatures, and exposure to various weather conditions.
What are Electrical Wire Color Codes?
When it comes to electrical work, safety is the top priority. A crucial part of ensuring safety is understanding the color codes used for electrical wires. Imagine the chaos if all the cables were the same color – It would be a nightmare to figure out which one does what!
Thankfully, there’s a standardized color-coding system that makes it easier for electricians to identify different wires and their functions.
Let’s break down the standard wire color designations:
- Hot (Live or Active): These are the wires that carry the electricity to power your devices. In North America, the standard color for hot wires is black. However, in some cases, a red wire might be used for a secondary hot conductor in a circuit. In three-phase systems, additional hot wires can be other colors like blue or yellow.
- Neutral: The neutral wire completes the circuit path for electricity to flow. It usually carries very little voltage relative to the ground and is designated by the colors white or grey.
- Ground: The ground wire provides a safety path for any stray current, protecting people and equipment from electrical shock. Ground wires are easy to identify by their color – green or green with a yellow stripe. They are typically bare (uninsulated) when used with metallic conduit.
Understanding these electrical wire color codes is crucial for anyone working with electrical systems. It’s the foundation for safe and efficient electrical work. By knowing what each color signifies, electricians can get the job done accurately. Color coding minimizes the risk of errors or accidents that could result from misidentifying wires.
What Things You Should Consider While Choosing an Electrical Wiring System?
The safety, efficiency, and functionality of your electrical system are crucial, so it’s essential to take the time to make informed decisions. Here are some key things to consider while choosing an electrical wiring system:
- Safety First – Ensure that the wiring system meets all safety standards and regulations. Look for products with built-in safety features, such as surge protection and fire-resistant materials.
- Capacity and Load – Consider the electrical load and capacity requirements of your space. Different areas of your home or business may have varying energy needs. So, it’s essential to choose a wiring system that can adequately support the electrical load without overloading the circuits.
- Flexibility and Future Expansion – An ideal electrical wiring system should allow for future expansions or modifications. Consider the flexibility of the system to accommodate additional electrical components or technological advancements without the need for extensive re-wiring.
- Energy Efficiency – In today’s world, energy efficiency is a key consideration for any electrical system. Look for wiring products that are designed to minimize energy wastage and maximize efficiency. This ultimately saves energy costs and reduces environmental impact.
- Durability and Longevity – Choose wiring materials that are resilient to wear and tear, weather-resistant, and capable of withstanding the demands of daily use.
- Compatibility With Smart Technology – It’s essential to choose an electrical wiring system that is compatible with innovative technology integration. This includes considerations for smart lighting, security systems, and other connected devices.
- Professional Installation and Maintenance – Lastly, always consult with qualified electricians for the installation and maintenance of your wiring system.
FAQ’s
-
Why is copper used for most electrical wiring?
Copper is used for most electrical wire because it is a great conductor of electricity, is highly ductile and malleable, is corrosion resistant, and has a high mechanical strength. Thus, it is suitable for conveying electrical currents effectively and safely in a variety of applications.
-
What do “L” and “N” mean in electrical wiring?
In electrical wiring, “L” often stands for “Line” or “Live” and refers to the phase or hot wire that transports electric current into a circuit. The letter “N” stands for “Neutral” and represents the current’s return channel to the electrical supply source. These designations are critical for adequately connecting electrical equipment and guaranteeing the safe operation of electrical systems.
-
What is the first stage of installing electrical wiring called?
The initial stage of installing electrical wiring is known as “rough-in” or “rough wiring.” Prior to the completion of the walls, ceilings, and floors, the primary electrical structure is erected. This comprises putting wires through the building or structure’s framework. It also includes situating electrical boxes and prepping for outlet, switch, and fixture connections. The rough-in stage guarantees that the electrical wire is in place and ready for the following stages of installation and connection.
-
How long does electrical wiring last?
Electrical wiring’s lifespan varies based on a number of factors, including installation quality, ambient conditions, and usage. In general, well-installed electrical wiring in residential settings may survive several decades, provided it is properly maintained and not subjected to extreme wear or damage. However, electrical wiring should be tested on a regular basis by competent personnel to verify its safety and conformity with current requirements.
-
Can bad wiring cause a high electric bill?
Yes, faulty wiring may result in a high electricity cost. It can cause energy loss due to resistance and poor electrical flow, leading to more electricity requirements for operating gadgets and appliances. Furthermore, faulty electrical connections can cause equipment to run inefficiently or overheat, leading to increased energy consumption.