Table of Contents
The quality and types of electrical wire determine how successful and efficient electrical systems are, whether they power your homes, workplaces, or educational institutions. When starting a building or repair project, it is just as important to comprehend the subtleties of electrical wires and understand the wire vs cable distinction as it is to grasp the difference between a Phillips and a flathead screwdriver.
It’s important to choose the right variety of wire for your needs because different types of electrical wire have different functions. Safety must also be taken into account while selecting electrical lines because poor choices can result in expensive and, more importantly—hazardous circumstances.
But you don’t need to worry- This blog post is here as your comprehensive guide for electrical wiring. Keep reading!
Basic Components of Electrical Wires
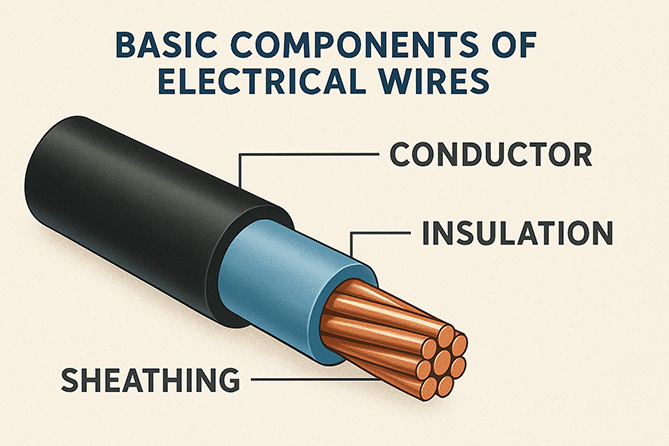
Let’s examine the basic elements of electrical lines before going into greater detail about their various varieties.
- Conductor: The essential component that permits the flow of electricity in an electrical line is the conductor. Usually, copper and aluminum are used in their construction. For the majority of applications, copper is the preferred material due to its exceptional electrical conductivity and durability. However, aluminum is more cost-effective and lighter. Moreover, it has particular applications in utility lines.
- Insulation: By encasing the conductor and protecting it from external elements like moisture and physical damage, insulation acts as a barrier. Rubber and polyvinyl chloride (PVC) are common insulating materials. Selecting the right insulation is essential since it influences the wire’s ability to operate in various environments. The thickness of the insulation also has a big influence on wire performance.
- Sheathing: Sheathing gives the wire an extra layer of defense, increasing its robustness and capacity to withstand outside forces. Common materials include thermosetting polymers, PVC, and polyethylene (PE). The sheathing is essential for the wire’s interior to stay insulated and shielded from potentially harmful elements.
Types of Electrical Wire
Electrical Wires come in a wide array of types, each designed for specific applications and environments. Some common types of electrical wire are:
-
THHN Wire
Usually utilized for construction wiring applications, THHN (Thermoplastic High-Temperature Nylon-coated) wire is made to withstand high temperatures. THHN wire is well-known for its adaptability and can be used in commercial, industrial, and residential contexts. Its resistance to abrasion and heat makes it extremely valuable.
-
THWN Wire
The main distinction between THHN and THWN (Thermoplastic Heat and Water-Resistant Nylon-coated) wire is that the former is appropriate for damp environments. When installing pumps and motors outdoors, where moisture can pose a safety risk, this wire is often used.
-
XHHW Wire
Cross-linked High-temperature Water-resistant, or XHHW, the wire has exceptional thermal stability and is impervious to chemicals and moisture. Because of its sturdy sheathing, it may be put underground and is commonly used in industrial settings. XHHW wire is ideal for applications requiring long-lasting underground or overhead performance.
-
MTW Wire
Machine Tool Wire, or MTW, is designed especially for use in appliances and machines. This kind can withstand the demands of motor-driven applications and is very versatile. MTW wire is often used in industrial settings because of its high temperature rating and water resistance.
-
Specialty Wires
Specialty wires are crafted for unique, often challenging applications that regular wires just can’t manage. Think about situations involving extreme heat, high voltage, or specialized conditions; that’s where these wires shine. Here are some of the examples:
- Thermocouple Wire: This wire is used to monitor temperature. It has two distinct conductors that work together to provide the thermoelectric effect that thermocouples require.
- Magnet Wire: Magnet wire is used in transformers and motors. It is insulated to permit heat dissipation, which is essential for the equipment it powers.
- Teflon Wire: Teflon wire, which is well-known for its high-temperature uses, is perfect for laboratory and aircraft environments since it can tolerate extremely high temperatures.
| Wire Type | Description | Features | Benefits | Typical Uses |
| THHN Wire | Thermoplastic High Heat-resistant Nylon-coated wire. | Heat-resistant, nylon coating, rated for dry and damp locations. | Durable, easy to install, cost-effective. | Residential and commercial wiring, conduit systems, control circuits. |
| THWN Wire | Thermoplastic Heat and Water-resistant Nylon-coated wire. | Water-resistant, heat-resistant, rated for wet and dry locations. | Versatile, suitable for indoor and outdoor use. | Outdoor wiring, underground conduits, service entrances. |
| XHHW Wire | Cross-linked Polyethylene High Heat-resistant and Water-resistant wire. | Excellent heat and moisture resistance, durable insulation. | Long lifespan, high durability, suitable for harsh environments. | Industrial wiring, commercial buildings, high-temperature applications. |
| MTW Wire | Machine Tool Wire designed for flexible use in machinery. | Oil-resistant, flexible, rated for dry locations. | High flexibility, resistant to oils and chemicals. | Machinery, appliances, control panels, and automation systems. |
| Thermocouple Wire | Wire used for temperature measurement in thermocouples. | High-temperature tolerance, accurate signal transmission. | Reliable temperature sensing, durable in extreme conditions. | Industrial temperature sensors, HVAC systems, scientific instruments. |
| Magnet Wire | Insulated wire used in electromagnets, motors, and transformers. | Thin insulation, high conductivity, thermal stability. | Efficient energy transfer, compact design. | Electric motors, transformers, inductors, and generators. |
| Teflon Wire | Wire insulated with Teflon (PTFE) for high-temperature and chemical resistance. | Extreme heat resistance, chemical inertness, low friction. | Suitable for harsh environments, long-lasting performance. | Aerospace, military, high-temperature industrial applications, medical devices. |
Electrical Wire Types: Depending on the Conductor Material
Additionally, wires are categorized according to the conductor material, which has a direct impact on their functionality, price, and applications. The most common conductivity materials are examined in further detail below.
-
Copper
If you are wondering what type of electrical wire is used in homes, your answer lies here! The industry standard is that copper wires are renowned for their exceptional flexibility and conductivity. Their dependability makes them perfect for household wiring, even though their initial cost may be higher.
-
Aluminum
Because it’s lightweight, aluminum is frequently used in overhead gearbox lines. Although it is less expensive than copper, installation requires more caution to prevent expansion and contraction hazards.
-
Copper-clad Aluminum
Aluminum wires coated with copper combine the advantages of both materials. They have outstanding conductivity and are reasonably priced. In low-voltage applications, this kind is becoming more and more popular.
-
Silver
Despite having the best conductivity of any metal, silver is too expensive for widespread use. It is mostly used in specialized fields such as high-frequency radio frequency electronics and aircraft.
-
Gold
Because gold wires don’t corrode, they are mostly found in high-end electronics and connectors. Their use is restricted to situations where the highest level of dependability is crucial due to their expensive cost.
-
Tinned Copper
The thin coating of tin on tinned copper on this wire improves corrosion resistance without sacrificing copper’s conductivity. In marine applications, where exposure to moisture is common, these types of wires are very advantageous.
-
Alloys Made of Nickel
Nickel alloys are selected for corrosive and high-temperature settings. They are used in situations where maintaining mechanical strength in challenging circumstances is necessary.
-
Steel
When high tensile strength is needed, like in messenger lines and grounding applications, steel wires are generally used.
-
Fiber-optic
Fibre optic cables are crucial to modern telecommunications because they allow data to be transmitted at light speed. Despite not being conventional electrical wires, they play an increasingly significant role in the electrical system.
| Wire Type | Conductivity | Cost | Applications |
| Copper | High | Moderate | General wiring, electronics |
| Aluminum | Moderate | Low | Power transmission, large-scale wiring |
| Copper-Clad Aluminum | Moderate | Low-Moderate | Audio cables, low-voltage applications |
| Silver | Very High | High | Specialized electronics, RF cables |
| Gold | Moderate | Very High | High-end electronics, connectors |
| Tinned Copper | High | Moderate | Marine, outdoor wiring |
| Nickel Alloys | Low-Moderate | Moderate-High | High-temperature environments |
| Steel | Low | Low | Overhead lines, grounding |
| Fiber Optic | N/A (Light) | High | Telecommunications, data networks |
Electrical Wire Types Depending on Conductor Structure
Electrical wires’ uses and performance qualities can also be determined by the conductor’s physical makeup.
-
Solid Wire
Solid wire is mostly utilized in fixed wiring applications and is made up of just one conductor. It is perfect for static circuits since it reduces the chance of overheating and power loss.
-
Stranded Wire
Stranded wire is flexible and easy to move since it is made up of several smaller wires that have been bundled together. It is typically used in devices like extension cords and portable equipment where the wire must bend or flex repeatedly.
| Feature | Solid Wire | Stranded Wire |
| Construction | Single, solid metal core | Multiple thin strands twisted together |
| Flexibility | Rigid, less flexible | Highly flexible |
| Resistance | Lower resistance | Higher resistance |
| Cost | Generally less expensive | Generally more expensive |
| Applications |
|
|
| Durability concerning bending | prone to breakage with repeated bending. | More durable when bending is required. |
Explore the difference in detail: Stranded vs Solid Wire.
How to Choose Electrical Wire?
Several important considerations should be at the forefront of your decision-making process when choosing electrical wires for your projects. Some of them are:-
- Environmental Conditions: Wires exposed to chemicals, high temperatures, or moisture must be appropriately selected to ensure longevity and safety.
- Safety Regulations and Adherence: Always ensure that your wiring conforms to local standards and laws to guard against any hazards and ensure dependability.
- Voltage and Current Capacity: Make sure the type of wire you choose can handle the voltage and current requirements of your application to prevent failure or overheating.
In the end, choosing electrical wires with efficiency and safety in mind can prevent issues later on and strengthen the integrity of your electrical systems.
You can make well-informed judgments for your industrial, commercial, or residential needs by being aware of the different types of wires that are available and the special advantages that each one provides.
Power your projects with top-quality electrical wires from D&F Liquidators.