Table of Contents
Discover essential electrical transformer maintenance checklists to ensure efficient energy flow and prevent costly faults via this comprehensive guide!
Imagine electricity as water flowing through a pipe. Transformers function similarly to special valves in the electricity grid’s pipelines. They can raise the pressure (voltage) of energy to allow for efficient long-distance transit, then lower it to a safe and controllable level to power your homes and appliances.
One of the things to remember is transformers, like your home’s plumbing, require frequent maintenance to function correctly. Maintenance of transformers prevents electrical faults and ensures that they perform properly without wasting energy. This not only saves money on maintenance but also prevents costly replacements in the long term.
This comprehensive blog is a guide to transformer maintenance, revealing the critical information you need to know to keep these wonderful machines functioning. So, let’s get started.
Transformer Components and Maintenance Schedule
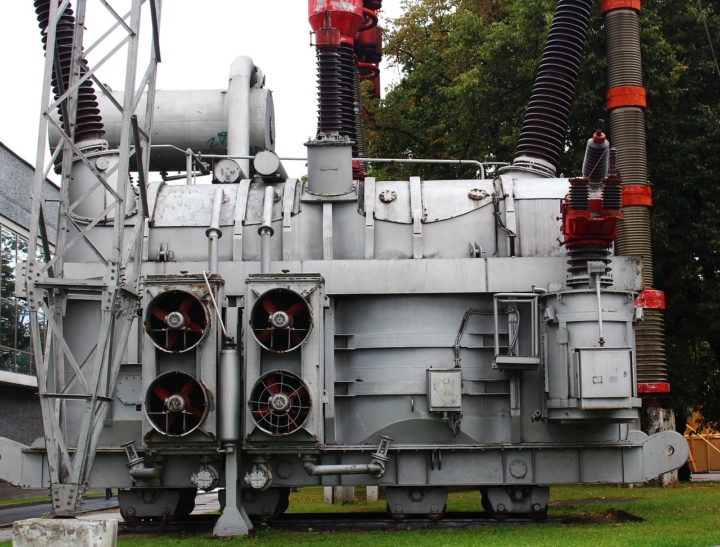
Transformers are crucial devices that transform electrical energy between voltage levels. They are made up of a variety of components, including coils, cores, and cooling systems. Coils, also known as windings, are essential for energy transfer.
The core, which is typically comprised of laminated steel, aids in decreasing energy losses. The cooling system prevents the transformer from overheating.
It is critical to adhere to a regular maintenance program. This includes inspecting and testing the components, looking for leaks and corrosion, and assuring adequate insulation. With the help of a robust maintenance plan, you can guarantee that your transformer runs smoothly and lasts as long as possible.
Transformers require two sorts of maintenance: preventive and ad hoc. Preventative maintenance is conducted on a regular basis to avoid problems from occurring. Ad-hoc maintenance, on the other hand, is performed as needed, typically in the event of an emergency or breakdown.
Regular condition maintenance allows technical professionals to avoid emergency repairs. When condition maintenance is done effectively, the likelihood of equipment breakdowns decreases dramatically.
To efficiently maintain a power transformer, several preventative activities must be conducted on a daily, monthly, quarterly, half-yearly, or yearly basis. Let’s check out how it’s done!
Electrical Transformer Maintenance Checklist
Daily Transformer Maintenance
- Transformer Oil: Transformers use oil as both an insulator and coolant. Daily inspections require evaluating the oil level and scanning for leaks.
- Bushings: Bushings provide entry and exit locations for electricity in transformers. Daily checks guarantee that these parts are free of fractures and grime.
- Cooling System: Keeping a transformer cool is critical. Check the cooling system, which includes fans or pumps, on a daily basis to ensure that it is functioning.
Monthly Transformer Maintenance Services
- Silica Gel Breather: Check the oil level in the cap beneath the silica gel breather every month. If the oil level is below the prescribed limit, top it off accordingly.
- Breathing Holes: Inspect the breathing holes in the silica gel breather monthly and clean them as needed to ensure proper airflow.
- Oil-Filled Bushings: Use the connected gauge to monitor the oil level in transformers with oil-filled bushings visually. Fill the bushings to the proper level, if necessary, under shutdown conditions.
Half-Yearly Transformer Maintenance
- Perform a 6-month oil check to examine dielectric strength, water content, acidity, sludge content, flash point, DDA, IFT, and resistance.
- There is often no need for further maintenance on distribution transformers that operate under light load situations.
Annual Transformer Maintenance and Services Schedule
- Cooling Components: Annually examine all cooling devices, including air fans and oil pumps, as well as control circuits.
- Bushing Cleaning: Wipe all transformer bushings with a soft cotton towel once a year.
- OLTC Oil Condition: Check the OLTC’s oil condition once a year. Take a sample of the drain valve and evaluate the moisture content (PPM) and dielectric strength (BDV). If the BDV is low or the PPM is high, replace the oil.
- Marshalling Boxes: Clean the interior of all marshaling boxes once a year. Ensure that the space and lighting heaters are working properly. Tighten all terminal connections on the control and relay wire at least once a year.
- Control System: Clean all control switches, alarms, relays, circuits, Remote Tap Changer Control Panel, and Relay and Control Panel using a suitable cleaning agent.
- Temperature Indicators: Check the oil levels in the pockets for both the Winding Temperature Indicator and the Oil Temperature Indicator. If required, add more oil.
- Buchholz Relay: Check the Buchholz and Press Release Device relays annually to ensure they are working correctly.
- Earth Connection: Use an earth resistance meter with a clamp to measure the resistive value of the earth connection and rizer once a year.
Additional Electrical Transformer Maintenance Checklist
- Dissolved Gas Analysis (DGA): DGA is a sophisticated test that analyses gases dissolved in oil to identify probable internal defects. Perform this test on a regular basis or as needed.
- Load Tap Changer (LTC): Depending on the kind and use, LTCs may require specialized maintenance inspections.
Transformers Defects and Their Root Cause
Power transformers can fail for different reasons. These faults might impact either exterior or interior components. Some of them are as follows:-
- Winding Failure: Winding failures happen for a variety of causes, including:
- Dielectric Faults: This refers to the breakdown of insulation between winding turns due to excessive voltage or current exceeding rated values. Insulation breakdown causes sparks between winding turns, resulting in short circuits.
- Thermal Losses: Windings are often constructed of copper; nevertheless, over time, inadequate maintenance can result in hot spots owing to copper line resistance. These hotspots cause wear and tear, which gradually diminishes physical strength until the windings break.
Mechanical Faults:
These include deformities such as loosening or replacing parts of the windings, which diminishes efficiency. Mechanical faults as following collectively distort turn-to-turn ratios, hampering performance.
- Poor maintenance
- Improper repairs
- Corrosion
- Manufacturing flaws
- Vibrations within the transformer
- Deterioration of Oil: Prolonged overloading increases oil temperature. This leads to the production of sludge and water vapor formation along with acid contamination. This phenomenon ultimately reduces the dielectric strength of the transformer.Oil deterioration can lead to several issues, such as dramatically increasing service life concerns, sparks, and significant malfunctions.
- Bushing Issues:
Bushings play a significant role in providing insulated paths for high-voltage conductors through earth-bound tank walls. In the transformer, it creates a current route through the tank wall. Insulators are used in transformer paper and are surrounded by oil to offer further insulation.Bushings might fail owing to incomplete discharge. This is sometimes due to the insulation’s slow and gradual breakdown over many years of use. Water intrusion, aging, or high dielectric losses all cause seal breakage in bushes. Because of this problem, the transformer’s core may fail.
Importance of Qualified Personnel for Transformer Maintenance Services
Transformer maintenance involves high-voltage electricity, posing significant risks such as electrical shock, arc flash explosions, and even death. Only trained and qualified personnel must handle transformer maintenance. These experts possess the necessary knowledge, skills, and safety equipment to perform the job safely and effectively.
Never attempt transformer maintenance yourself or assign the task to someone without the proper qualifications. By relying on qualified personnel, you ensure the safety of everyone involved and protect valuable equipment.
In conclusion, maintaining transformers is akin to ensuring the smooth flow of electricity through a well-maintained pipeline system. Just as regular plumbing checks prevent water leaks and burst pipes, consistent transformer maintenance prevents electrical faults and ensures peak performance.
This guide has walked you through the essential components, maintenance schedules, and types of maintenance required to keep transformers in top shape. Equip yourself with this knowledge, and let’s keep those electrical valves running smoothly!